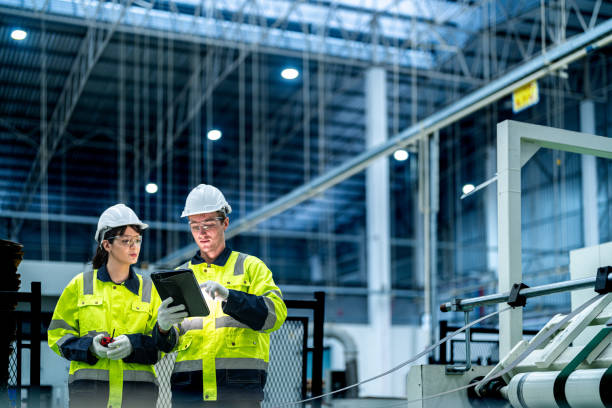
Anti-Corrosion Methods for High-Humidity Environments
Discover effective rust prevention strategies for wet climates, where constant moisture can damage vehicles, tools, and structures. Protective coatings, regular cleaning, and proper storage help shield metal surfaces, extending their lifespan and maintaining strength in challenging weather conditions.
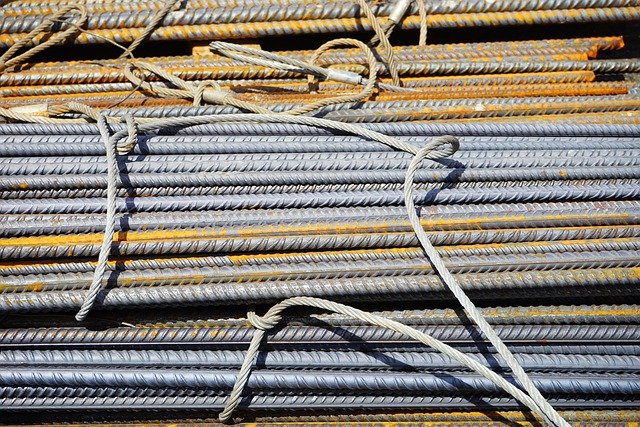

What Are the Most Effective Rust Prevention Methods for Wet Climates?
Barrier coatings represent one of the most reliable rust prevention methods for wet climates. These protective layers include galvanizing, powder coating, and specialized marine-grade paints that create physical barriers between metal surfaces and moisture. Galvanized steel, coated with zinc, provides excellent protection as the zinc corrodes preferentially, protecting the underlying steel. Powder coating offers superior adhesion and durability compared to traditional liquid paints, making it ideal for outdoor equipment and structural components.
Cathodic protection systems work by making the metal structure the cathode in an electrochemical cell, preventing corrosion at the molecular level. This method proves particularly effective for underground pipes, marine structures, and large industrial installations. Sacrificial anodes, typically made of zinc or magnesium, corrode instead of the protected metal, while impressed current systems use external power sources to maintain protective electrical currents.
How Do Environmental Factors Influence Rust Prevention Tips?
Humidity levels directly impact corrosion rates, with relative humidity above 60% significantly accelerating rust formation. Temperature fluctuations create condensation cycles that repeatedly wet and dry metal surfaces, intensifying oxidation processes. Salt air in coastal regions compounds these effects, as chloride ions accelerate electrochemical reactions that cause corrosion.
Proper ventilation and moisture control become essential rust prevention tips in wet climates. Installing dehumidifiers in enclosed spaces, ensuring adequate air circulation around metal components, and using moisture-absorbing materials like silica gel packets can dramatically reduce corrosion rates. Regular cleaning to remove salt deposits, dirt, and other contaminants prevents the formation of localized corrosion cells that lead to pitting and structural damage.
Which Rust Prevention Solutions Work Best for Wet Climates?
Corrosion inhibitors offer chemical rust prevention solutions for wet climates by forming protective molecular films on metal surfaces. Volatile corrosion inhibitors (VCIs) provide protection in enclosed spaces by releasing vapor-phase compounds that settle on metal surfaces, creating invisible protective barriers. These prove particularly effective for stored equipment, spare parts, and seasonal machinery.
Stainless steel alloys containing chromium, nickel, and molybdenum provide inherent corrosion resistance through passive oxide layers that self-repair when damaged. Marine-grade aluminum alloys offer excellent corrosion resistance while maintaining lightweight properties for applications where weight matters. These material choices, while requiring higher initial investment, often prove cost-effective over extended periods in challenging environments.
Selecting appropriate anti-corrosion solutions requires balancing initial costs, maintenance requirements, and expected service life. Professional assessment of environmental conditions, material compatibility, and application-specific needs ensures optimal protection strategies. Regular inspection and maintenance programs maximize the effectiveness of any chosen rust prevention method, helping identify potential issues before they become costly problems. Understanding these principles empowers property owners and facility managers to make informed decisions about protecting their metal assets in challenging wet climate conditions.