Atopic Dermatitis: Complete Guide to Symptoms and Treatment
Struggling with itchy, irritated skin? Atopic dermatitis treatments range from moisturizers and lifestyle changes to prescription options. Consult a dermatologist to explore personalized solutions for long-term comfort and relief. Read more about atopic dermatitis to see which treatment best suits you.
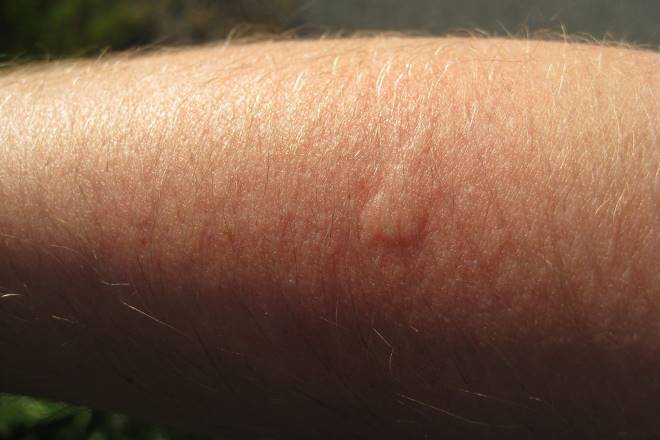
What Is Atopic Dermatitis?
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin patches. This condition typically begins in childhood but can persist into adulthood or even develop later in life. The term “atopic” refers to a tendency to develop allergic conditions, while “dermatitis” simply means inflammation of the skin.
The condition occurs when the skin’s natural barrier function becomes compromised, allowing moisture to escape and irritants to penetrate more easily. This leads to the characteristic symptoms that define atopic dermatitis. Unlike contact dermatitis, which results from direct exposure to irritants, atopic dermatitis stems from internal factors including genetics, immune system dysfunction, and environmental triggers.
Common Atopic Dermatitis Symptoms
Atopic dermatitis symptoms can vary significantly between individuals and may change over time. The most prevalent symptom is intense itching, which often worsens at night and can disrupt sleep patterns. This persistent itching creates a cycle where scratching leads to further skin damage and inflammation.
Visible signs include red, inflamed patches of skin that may appear scaly or rough. In acute flares, the skin might develop small, fluid-filled bumps that can weep or crust over. Chronic atopic dermatitis often results in thickened, leathery skin from repeated scratching, a condition called lichenification.
The location of symptoms typically depends on age. Infants commonly experience atopic dermatitis on their face, scalp, and outer surfaces of arms and legs. Adults more frequently develop symptoms in skin folds, including the inner elbows, behind knees, neck, and around the eyes. Some individuals may experience widespread involvement across multiple body areas.
Effective Atopic Dermatitis Treatment Options
Successful atopic dermatitis treatment typically involves a multi-faceted approach combining topical medications, lifestyle modifications, and trigger avoidance. The treatment strategy should be tailored to the individual’s severity, age, and specific triggers.
Topical corticosteroids remain the first-line treatment for active inflammation. These medications come in various strengths, from mild hydrocortisone for sensitive areas to stronger preparations for thick, stubborn patches. Newer non-steroidal topical medications, including calcineurin inhibitors like tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, offer effective alternatives without the long-term side effects associated with prolonged steroid use.
For moderate to severe cases, systemic treatments may be necessary. Oral corticosteroids can provide rapid relief during severe flares, though they’re typically used short-term due to potential side effects. Newer biologic medications, such as dupilumab, target specific immune pathways involved in atopic dermatitis and have shown remarkable success in clinical trials.
Managing Triggers and Prevention Strategies
Identifying and avoiding personal triggers plays a crucial role in managing atopic dermatitis effectively. Common triggers include certain fabrics, harsh soaps, extreme temperatures, stress, and specific foods. Keeping a symptom diary can help identify patterns and potential triggers unique to each individual.
Environmental modifications can significantly reduce flare-ups. Using fragrance-free, hypoallergenic products for bathing and laundry helps minimize skin irritation. Maintaining optimal humidity levels in living spaces, especially during winter months, prevents excessive skin drying. Wearing soft, breathable fabrics like cotton while avoiding wool and synthetic materials can reduce friction and irritation.
Stress management techniques, including meditation, regular exercise, and adequate sleep, can help reduce the frequency and severity of flares. Since stress is a common trigger for atopic dermatitis, developing healthy coping mechanisms becomes an essential component of long-term management.
Professional Treatment Costs and Provider Options
Understanding the financial aspects of atopic dermatitis treatment helps patients make informed decisions about their care. Treatment costs vary significantly depending on the severity of the condition, chosen treatments, and insurance coverage.
| Treatment Type | Provider | Average Cost Range |
|---|---|---|
| Dermatologist Consultation | Private Practice | $200-$400 per visit |
| Topical Prescription Medications | Pharmacy/Insurance | $20-$150 per month |
| Biologic Therapies | Specialty Pharmacy | $2,000-$4,000 per month |
| Phototherapy Sessions | Dermatology Clinics | $75-$200 per session |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Insurance coverage varies widely, with many plans covering basic topical treatments but requiring prior authorization for newer biologic medications. Patient assistance programs offered by pharmaceutical companies can significantly reduce costs for qualifying individuals. Generic alternatives for many topical medications can provide substantial savings while maintaining effectiveness.
Building Your Long-Term Management Plan
Developing a comprehensive, long-term management plan with healthcare providers ensures optimal outcomes for atopic dermatitis. This plan should include both acute treatment strategies for flares and maintenance approaches to prevent future episodes.
Regular follow-up appointments allow for treatment adjustments based on response and seasonal changes. Many patients benefit from step-up and step-down treatment protocols, intensifying therapy during flares and maintaining minimal effective treatment during clear periods. Patient education about proper skincare techniques, including gentle cleansing and regular moisturizing, forms the foundation of any successful management plan.
Working with dermatologists, allergists, and other specialists when necessary provides access to the most current treatment options and clinical trials. Support groups and educational resources can provide valuable practical tips and emotional support for managing this chronic condition.
Atopic dermatitis management requires patience, consistency, and often multiple treatment approaches to achieve optimal control. With proper understanding of the condition, appropriate treatment, and lifestyle modifications, most individuals can achieve significant improvement in their symptoms and quality of life.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.




