Autoimmune Scalp Conditions: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Autoimmune scalp conditions, such as alopecia areata or lupus-related hair loss, occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy hair follicles. This can lead to patchy bald spots, scalp inflammation, redness, or scaling. Managing these conditions often involves a combination of medication, stress reduction, and gentle scalp care to help soothe symptoms and support hair regrowth.
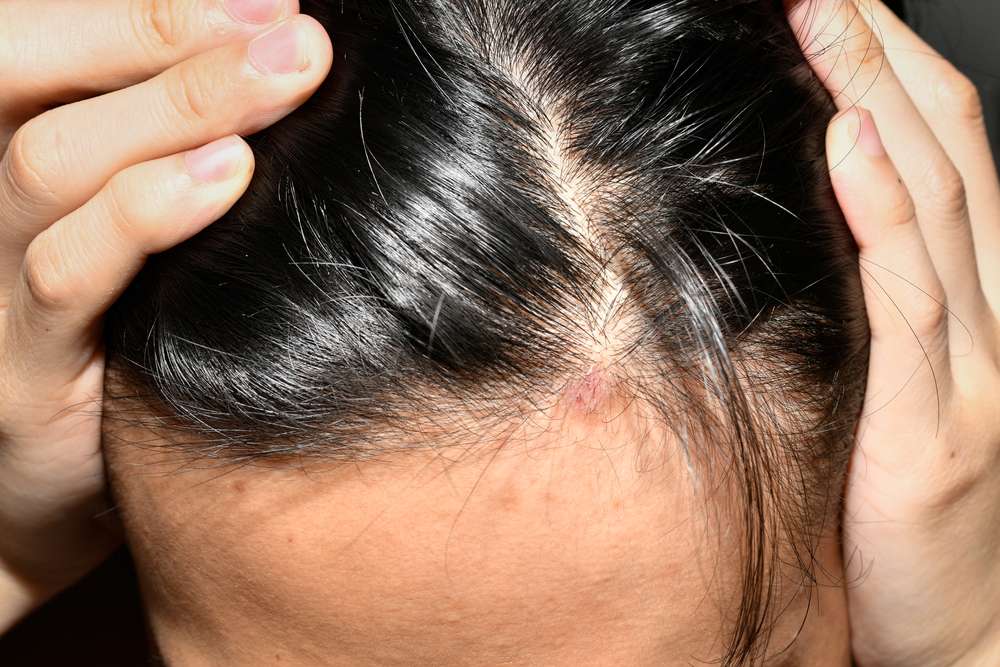
What are the most common autoimmune diseases that affect the scalp?
Several autoimmune diseases can impact the scalp, causing a range of symptoms from mild irritation to significant hair loss. Some of the most prevalent conditions include:
-
Alopecia Areata: This condition causes patchy hair loss on the scalp and other parts of the body. It occurs when the immune system attacks hair follicles, leading to sudden hair loss in circular patches.
-
Lupus: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) can affect various parts of the body, including the scalp. It may cause hair thinning, scalp lesions, and a distinctive scarring alopecia known as discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE).
-
Psoriasis: While primarily affecting the skin, psoriasis can also manifest on the scalp, causing red, scaly patches and potential hair loss in severe cases.
-
Lichen Planopilaris: This inflammatory condition primarily affects the scalp, causing progressive hair loss and scarring.
-
Pemphigus Vulgaris: A rare autoimmune disorder that can cause painful blisters on the scalp and other parts of the body.
How do autoimmune scalp conditions lead to hair loss?
Autoimmune scalp conditions can cause hair loss through various mechanisms:
-
Direct follicle damage: In conditions like alopecia areata, the immune system directly attacks hair follicles, disrupting normal hair growth cycles.
-
Inflammation: Chronic inflammation in conditions such as lupus or psoriasis can damage hair follicles and inhibit hair growth.
-
Scarring: Some autoimmune conditions, like lichen planopilaris, can cause scarring of the scalp, permanently destroying hair follicles and preventing regrowth.
-
Systemic effects: In systemic autoimmune diseases like lupus, overall health deterioration and medication side effects can contribute to hair thinning and loss.
-
Stress: The physical and emotional stress associated with managing an autoimmune condition can exacerbate hair loss.
What are the signs of autoimmune disease on the scalp?
Recognizing the signs of autoimmune disease on the scalp is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. Common symptoms include:
-
Patchy hair loss: Sudden loss of hair in circular or irregular patches, often smooth to the touch.
-
Scalp redness and inflammation: Visible redness, swelling, or warmth on the scalp.
-
Scaling or flaking: Dry, scaly patches that may be itchy or painful.
-
Scarring: Areas of smooth, shiny skin where hair follicles have been destroyed.
-
Changes in hair texture: Hair may become brittle, thin, or break easily.
-
Scalp sensitivity: Increased tenderness or pain when touching the scalp.
-
Blisters or sores: In some conditions, painful blisters or open sores may develop on the scalp.
-
Systemic symptoms: Fatigue, joint pain, or other body-wide symptoms that may accompany scalp issues.
How are autoimmune scalp conditions diagnosed?
Diagnosing autoimmune scalp conditions typically involves a combination of approaches:
-
Physical examination: A dermatologist or trichologist will closely examine the scalp and hair for characteristic signs of autoimmune conditions.
-
Medical history: A thorough review of the patient’s medical history, including family history of autoimmune diseases, is essential.
-
Scalp biopsy: In some cases, a small sample of scalp tissue may be taken for microscopic examination to confirm the diagnosis.
-
Blood tests: Specific blood tests can help identify autoantibodies associated with certain autoimmune conditions.
-
Trichoscopy: This non-invasive technique uses a special magnifying device to examine the scalp and hair shafts in detail.
-
Punch biopsy: For conditions like lichen planopilaris, a punch biopsy may be necessary to assess the extent of scarring.
What treatment options are available for autoimmune scalp conditions?
Treatment for autoimmune scalp conditions often requires a multifaceted approach:
-
Topical treatments: Corticosteroid creams or ointments can help reduce inflammation and promote hair regrowth in some cases.
-
Systemic medications: Immunosuppressants or biologics may be prescribed for more severe or widespread conditions.
-
Intralesional injections: Corticosteroids can be injected directly into affected areas to stimulate hair growth.
-
Light therapy: Treatments like excimer laser or phototherapy may be effective for certain conditions.
-
Scalp care: Gentle cleansing and moisturizing can help manage symptoms and promote a healthy scalp environment.
-
Hair camouflage: For extensive hair loss, wigs, hairpieces, or scalp micropigmentation can provide cosmetic solutions.
-
Stress management: Techniques like meditation, yoga, or counseling can help manage the emotional impact of these conditions.
-
Dietary changes: Some patients may benefit from an anti-inflammatory diet or specific nutritional supplements.
How can patients cope with the emotional impact of autoimmune scalp conditions?
Living with an autoimmune scalp condition can be emotionally challenging. Patients can cope by:
-
Seeking support: Joining support groups or connecting with others who have similar conditions can provide emotional comfort and practical advice.
-
Exploring styling options: Working with a stylist experienced in hair loss can help find flattering hairstyles or headwear options.
-
Practicing self-care: Engaging in activities that boost self-esteem and overall well-being is crucial.
-
Communicating openly: Discussing concerns with healthcare providers, friends, and family can help address emotional needs.
-
Considering therapy: Professional counseling can provide strategies for managing the psychological impact of hair loss and chronic illness.
Autoimmune scalp conditions can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, but with proper diagnosis and treatment, many patients can manage their symptoms effectively. It’s essential to work closely with healthcare providers to develop a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to individual needs. While these conditions can be challenging, ongoing research and new treatment options offer hope for improved outcomes in the future.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.




