Foods That Burn Belly Fat: Science-Based Options for Your Diet
Certain foods, when paired with a healthy lifestyle, may support fat metabolism and digestive health. Explore options such as fiber-rich vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains that are commonly included in balanced meal plans for wellness. Read this to learn what foods help burn fat.
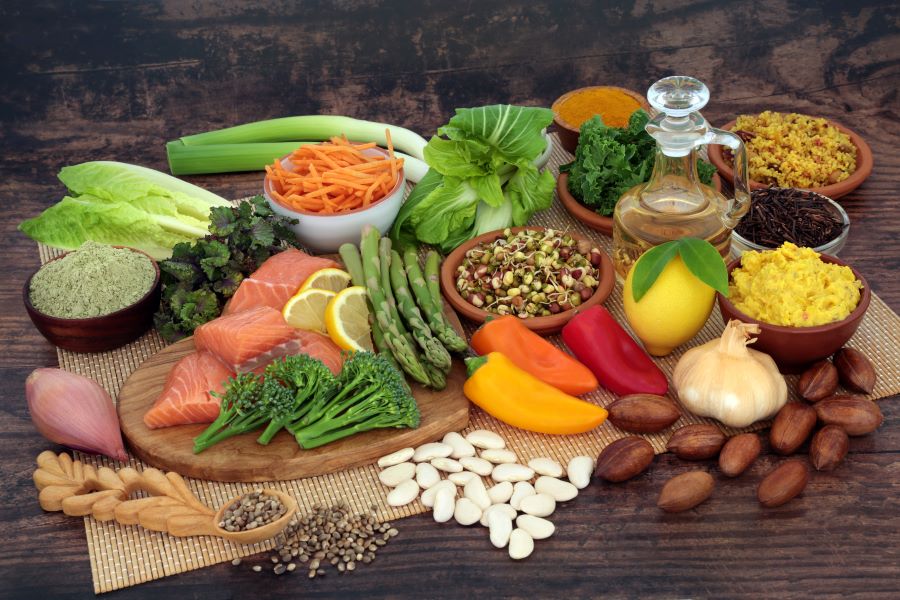

Foods Rich in Fiber for Belly Fat Reduction
Dietary fiber plays a crucial role in weight management and specifically in reducing belly fat. Soluble fiber absorbs water and forms a gel-like substance in your digestive tract, slowing digestion and increasing feelings of fullness. Research published in the journal Obesity found that for every 10-gram increase in soluble fiber intake, visceral fat accumulation decreased by 3.7% over five years. Excellent sources include legumes (beans, lentils, chickpeas), flaxseeds, and vegetables like brussels sprouts and broccoli. These foods not only help you feel satisfied longer but also regulate blood sugar levels, preventing insulin spikes that can lead to fat storage around the midsection.
Protein-Packed Foods That Target Fat Storage
Lean protein sources deserve a prominent place in any belly fat reduction plan. Protein requires more energy to digest than carbohydrates or fats (the thermic effect), temporarily boosting metabolism by 15-30%. Studies show that high-protein diets help preserve muscle mass during weight loss, which keeps your metabolic rate higher. Options like skinless chicken breast, fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), Greek yogurt, eggs, and plant proteins like tofu and tempeh make excellent choices. The Journal of Nutrition reports that higher protein intake is associated with less abdominal fat and better weight maintenance over time. Aim to include a quality protein source at each meal to maximize these benefits.
Healthy Fats That Actually Help Burn Fat
Contrary to older dietary recommendations, certain fats can actually help reduce belly fat when consumed in appropriate portions. Monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) and polyunsaturated fats, particularly omega-3s, have been shown to reduce inflammation and lower cortisol levels—both factors linked to abdominal fat storage. Avocados, olive oil, nuts (especially almonds and walnuts), and seeds provide beneficial MUFAs. Meanwhile, fatty fish like salmon and sardines deliver potent omega-3s. A study in Diabetes Care found that participants who included these healthy fats in their diets experienced greater reductions in belly fat compared to those on low-fat diets with the same calorie content. The key is replacing saturated fats with these healthier options rather than simply adding more fat to your diet.
Metabolism-Boosting Beverages and Spices
Certain beverages and spices can temporarily increase metabolic rate, potentially supporting fat loss when combined with other healthy habits. Green tea contains both caffeine and catechins, plant compounds that may increase energy expenditure and fat oxidation. Research in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition suggests drinking 2-3 cups daily may help with modest weight and fat loss. Similarly, spices like cayenne pepper contain capsaicin, which increases calorie burning and may reduce appetite. Adding cinnamon to meals can help stabilize blood sugar levels, preventing spikes that lead to fat storage. While these metabolism boosters won’t create dramatic changes alone, they can enhance results when part of a comprehensive approach to nutrition.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods for Stubborn Belly Fat
Chronic inflammation is increasingly recognized as a key contributor to belly fat accumulation. Foods with anti-inflammatory properties may therefore help address this underlying cause. Berries (especially blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries) contain powerful antioxidants called polyphenols that fight inflammation. Leafy greens like kale and spinach provide essential nutrients that combat oxidative stress. Turmeric contains curcumin, which studies show has significant anti-inflammatory effects. Fermented foods like kimchi, sauerkraut, and kefir support gut health, which is increasingly linked to reduced inflammation and healthier weight management. Regular consumption of these anti-inflammatory foods may help reduce the inflammatory response that contributes to stubborn abdominal fat.
Complex Carbohydrates That Support Fat Loss
Not all carbohydrates promote weight gain—whole, unprocessed complex carbs can actually support fat loss when eaten in appropriate portions. These foods contain resistant starch and fiber that feed beneficial gut bacteria, potentially improving metabolism and reducing fat storage. Oats contain beta-glucans that increase satiety hormones and improve insulin sensitivity. Sweet potatoes provide filling fiber plus nutrients that support fat metabolism. Ancient grains like quinoa and buckwheat offer complete proteins along with complex carbohydrates. Brown rice provides manganese, a mineral that helps your body metabolize fats. When replacing refined carbohydrates with these nutrient-dense alternatives, most people naturally consume fewer calories while feeling more satisfied, creating conditions favorable for fat loss around the midsection.
Conclusion
While no single food can specifically target belly fat, incorporating these evidence-backed options into your overall healthy eating pattern can support your body’s natural fat-burning processes. The key to success lies in consistency and combining these nutritional choices with regular physical activity, adequate sleep, and stress management. Remember that sustainable weight loss typically happens gradually, at a rate of 1-2 pounds per week, with reductions in belly fat following this same pattern. Rather than focusing on quick fixes, build a sustainable eating pattern rich in these beneficial foods to create lasting changes in both your appearance and health.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.