Hearing Aids: Tips for Selecting the Right Device
Finding the ideal hearing aid involves more than simply choosing a model—it's about understanding how different technologies support your specific hearing needs and daily activities. This guide walks you through the essential factors to consider, from sound quality and comfort to features like noise reduction and connectivity. With practical advice and easy-to-follow insights, you can confidently select a device that enhances your hearing experience and fits seamlessly into your lifestyle.
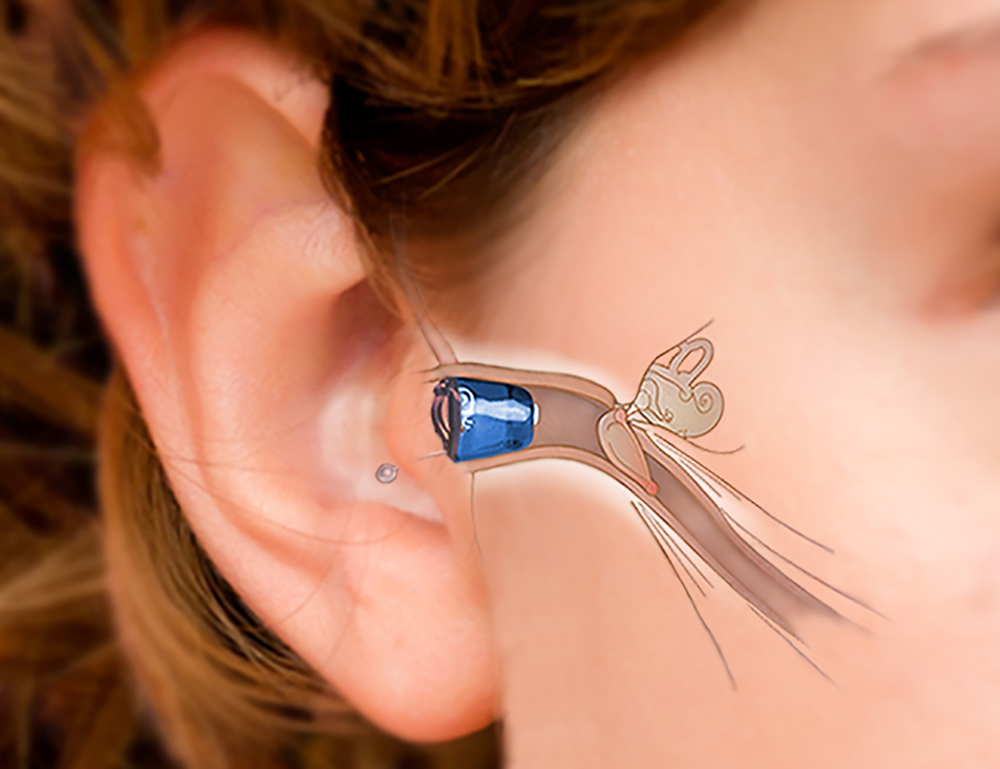
Understanding Different Hearing Aid Types
Hearing aids come in various styles, each designed to address different degrees of hearing loss and user preferences. Behind-the-Ear (BTE) models are among the most common, featuring a case that rests behind the ear connected to a custom earmold or a thin tube. These are often robust and suitable for a wide range of hearing losses, including severe cases. Receiver-in-Canal (RIC) or Receiver-in-the-Ear (RITE) aids are similar to BTEs but have the speaker (receiver) placed directly in the ear canal, connected by a thin wire. This design often results in a smaller, less noticeable device with excellent sound quality.
In-the-Ear (ITE) hearing aids are custom-made to fit within the outer ear bowl. They are larger than some other custom options, making them easier to handle for individuals with dexterity challenges, and can accommodate features like directional microphones or volume controls. Completely-in-the-Canal (CIC) and Invisible-in-the-Canal (IIC) aids are the smallest and most discreet, fitting entirely or almost entirely within the ear canal. While offering significant cosmetic appeal, their small size means they may have shorter battery life and fewer features, and might not be suitable for severe hearing loss.
Factors in Choosing Hearing Aids
Choosing the right hearing aid involves evaluating several personal and technical factors. The degree and type of hearing loss, as determined by an audiological evaluation, is the primary consideration. Different hearing aids are optimized for specific ranges of hearing loss. Lifestyle also plays a significant role; an active individual who frequently attends social events or works in noisy environments might benefit from advanced features like noise reduction and directional microphones, while someone with a quieter lifestyle may prioritize comfort and ease of use.
Personal preferences regarding aesthetics, comfort, and manual dexterity are also important. Some individuals prefer the discretion of smaller in-canal models, while others might find BTE or ITE devices easier to manage, especially if they have limited finger dexterity. Battery life, rechargeable options, and connectivity features (such as Bluetooth for streaming from smartphones or televisions) are additional considerations that can enhance the user experience and overall satisfaction with the device. Consulting with an audiology professional can help navigate these options effectively, ensuring the chosen device aligns with individual needs and expectations.
Insights into Hearing Aid Cost
The cost of hearing aids can vary significantly based on technology level, features, style, and the professional services included. Generally, devices with more advanced features, such as sophisticated noise reduction algorithms, Bluetooth connectivity, and rechargeable batteries, tend to be at the higher end of the price spectrum. Entry-level models typically provide essential amplification and can be more budget-friendly. It is important to remember that the price often includes not just the device itself, but also professional services like initial fitting, follow-up adjustments, and warranties, which are crucial for optimal performance and user satisfaction.
When considering the investment, it is advisable to inquire about what is included in the overall cost. Some providers offer bundled packages that cover several years of professional care, while others may itemize services separately. Exploring options with local services and comparing offerings can provide a clearer picture of the total expenditure. Some insurance plans may offer partial coverage, and flexible payment plans or financing options might be available through various providers or third-party organizations to help manage the financial commitment.
| Type of Aid/Service | Provider/Brand Example | Estimated Cost Range (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Entry-Level Digital Aids | Local Audiology Clinics | $1,000 - $3,000 per aid |
| Mid-Range Digital Aids | Major Brands (e.g., Phonak, Oticon) | $2,500 - $5,000 per aid |
| Advanced Digital Aids | Premium Brands | $4,000 - $7,000+ per aid |
| Over-the-Counter (OTC) Aids | Retailers (e.g., Jabra Enhance, Lexie) | $200 - $2,000 per pair |
| Professional Fitting & Services | Independent Audiologists | Included in aid cost or separate fee |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Selecting the appropriate hearing aid is a significant decision that impacts an individual’s quality of life and communication abilities. By understanding the different types of devices, considering personal needs and lifestyle, and gaining insight into the associated costs, individuals can approach the selection process with greater confidence. Professional guidance from an audiologist is invaluable in navigating the complexities of hearing aid technology and ensuring the chosen device provides effective and comfortable hearing support.