Laser Engraving: How It Works and Its Applications
Discover how laser engraving works and why it’s a popular choice for crafting and personalization. From detailed designs to custom gifts, this technology allows creators to achieve precise, professional results, making projects more creative, unique, and visually impressive.
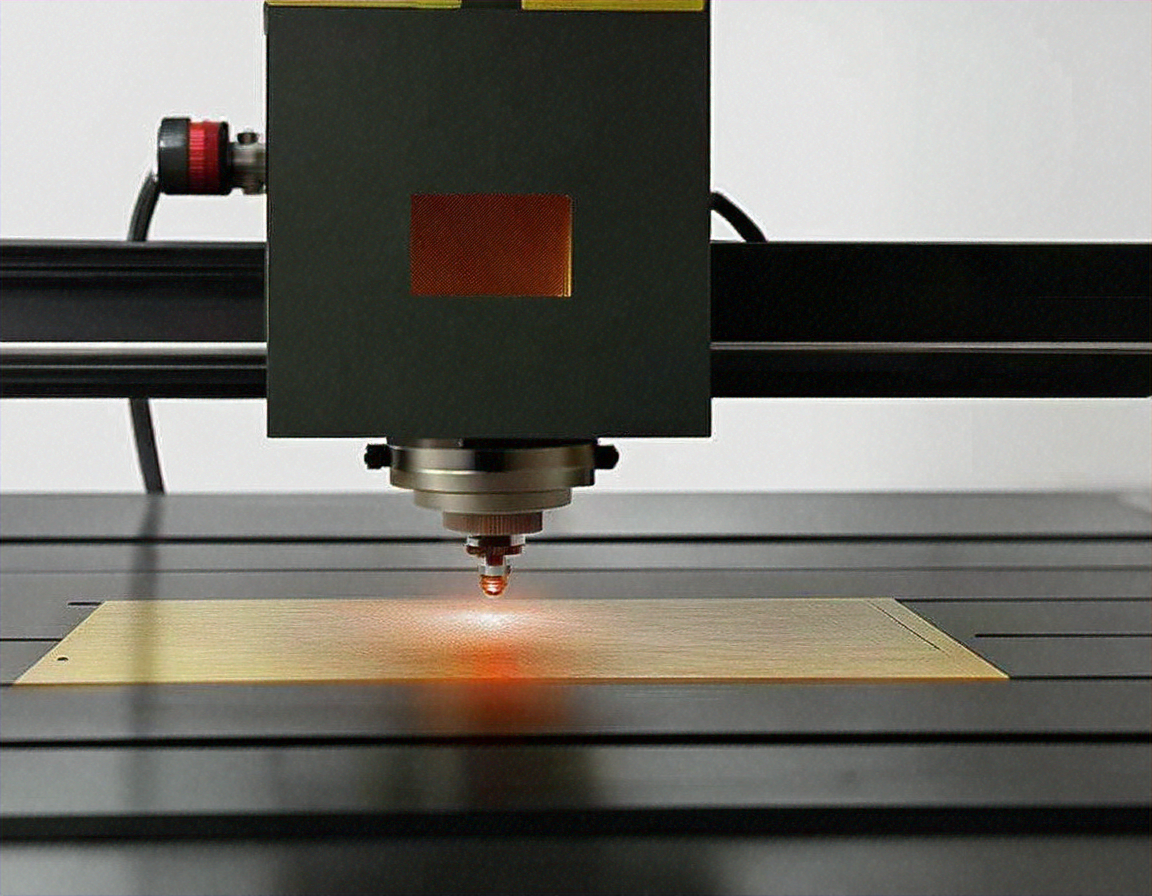
How Does Laser Engraving Work?
Laser engraving operates on a relatively simple principle: a highly focused beam of light is directed onto a material’s surface, causing it to heat up and vaporize. This process creates a permanent indentation or mark on the material. The laser beam is controlled by computer software, allowing for precise and repeatable designs. The depth and quality of the engraving depend on factors such as the laser’s power, the material being engraved, and the speed at which the beam moves across the surface.
What Are the Main Components of a Laser Engraving System?
A typical laser engraving system consists of several key components working together to produce the desired result. The laser source generates the intense beam of light, which is then directed through a series of mirrors and lenses. These optical elements focus and guide the beam onto the workpiece. A computer-controlled motion system moves either the laser or the material being engraved to create the design. Safety features, such as enclosures and exhaust systems, are also crucial parts of professional laser engraving setups.
Which Materials Can Be Laser Engraved?
Laser engraving is remarkably versatile when it comes to compatible materials. Wood is a popular choice due to its natural aesthetic and ease of engraving. Metals like aluminum, stainless steel, and brass can also be engraved, often requiring more powerful lasers. Glass and acrylic offer unique possibilities for creating transparent or translucent designs. Other materials suitable for laser engraving include leather, stone, and certain plastics. However, it’s important to note that some materials, such as PVC, should not be laser engraved due to the release of harmful fumes.
What Are the Different Types of Laser Engraving Machines?
There are several types of laser engraving machines, each suited for different applications and materials. CO2 lasers are versatile and commonly used for engraving organic materials like wood, leather, and acrylic. Fiber lasers excel at engraving metals and are often used in industrial settings. Crystal lasers, such as Nd:YAG lasers, offer high precision and are suitable for both metals and non-metals. Desktop laser engravers have gained popularity for small businesses and hobbyists, providing a compact and affordable option for lighter engraving tasks.
How Does Laser Engraving Compare to Other Marking Methods?
Laser engraving offers several advantages over traditional marking methods like mechanical engraving or chemical etching. It provides higher precision and the ability to create intricate designs with minimal material waste. Laser engraving is also a non-contact process, reducing wear on tools and allowing for the marking of delicate or irregularly shaped objects. However, the initial cost of laser engraving equipment can be higher than that of some traditional methods. The choice between laser engraving and other techniques often depends on factors such as material compatibility, production volume, and desired finish quality.
What Are the Applications of Laser Engraving in Industry and Art?
Laser engraving finds applications across a wide range of industries and artistic endeavors. In manufacturing, it’s used for part marking, serial number engraving, and creating functional textures on surfaces. The jewelry industry employs laser engraving for personalization and intricate designs. Artists and craftspeople use the technology to create unique pieces on various materials, pushing the boundaries of traditional engraving techniques. In the promotional products sector, laser engraving adds value to items like pens, awards, and electronic devices through customization.
| Application | Industry | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Part Marking | Manufacturing | Serial numbers, barcodes, logos |
| Personalization | Jewelry | Custom engravings, name plates |
| Artistic Creation | Fine Arts | Intricate designs on wood, glass |
| Product Customization | Promotional Products | Engraved pens, awards, gadgets |
| Functional Texturing | Industrial Design | Grip patterns, anti-slip surfaces |
Laser engraving technology continues to evolve, offering new possibilities for both industrial and creative applications. As the process becomes more accessible and versatile, it opens up opportunities for businesses and individuals to explore unique ways of adding value and personalization to a wide range of products and materials. Whether for practical marking purposes or artistic expression, laser engraving remains a powerful tool in the realm of surface modification and design.




