Understanding Gynecomastia: Symptoms, Warning Signs, and Treatment Options
Learn about the prodromes of gynecomastia and how early signs like breast tenderness or swelling relate to managing breast pain. Recognizing these initial changes can help guide appropriate care, easing discomfort while understanding underlying causes for more informed treatment decisions.
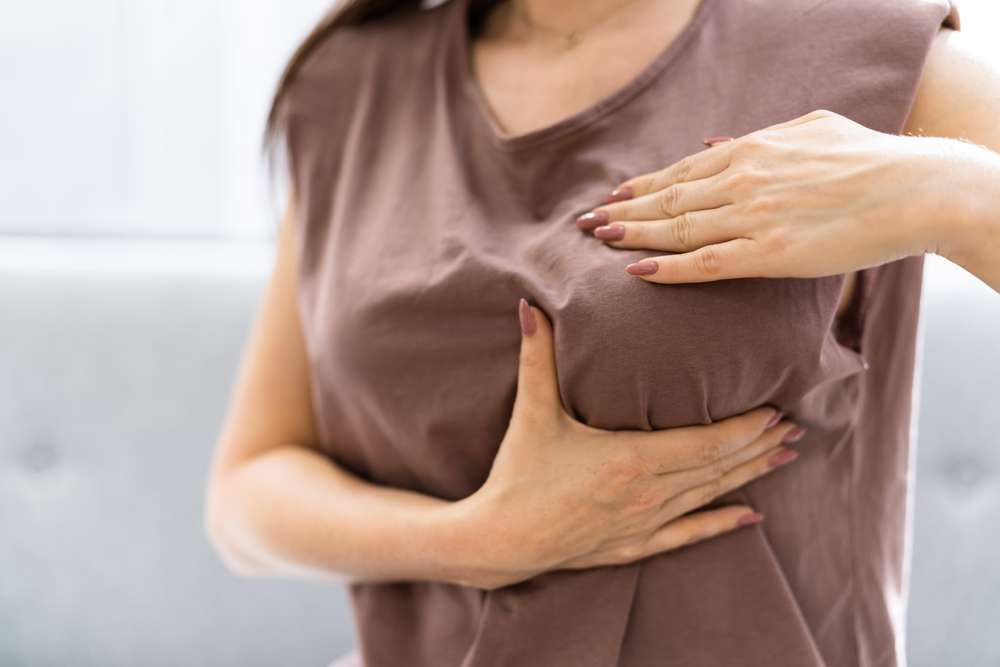

Symptoms and Prodromes of Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia typically develops gradually, with several recognizable prodromes appearing before full manifestation. The earliest indication is often a small, firm mass of tissue centered beneath the nipple area, approximately the size of a coin. This tissue may be tender or sensitive to touch. Patients frequently report a rubbery or firm texture to this tissue, distinguishing it from surrounding fat. Another early sign is bilateral breast enlargement, though asymmetrical development (affecting one breast more than the other) occurs in approximately 20% of cases. These initial changes may be subtle enough that some men don’t immediately recognize them as problematic.
As the condition progresses, more noticeable symptoms include increased breast volume, continued tenderness, and occasionally nipple discharge in advanced cases. Some men also report sensations of heaviness in the chest area. It’s important to note that not all breast enlargement in men is true gynecomastia—pseudogynecomastia, characterized by fat deposition without glandular development, presents differently and requires different treatment approaches.
Gynecomastia Warning Signs to Watch For
Several warning signs indicate when medical attention should be sought for gynecomastia. Rapid breast tissue growth, particularly when unilateral (affecting only one side), warrants prompt evaluation as it may indicate an underlying condition requiring immediate treatment. Similarly, breast growth accompanied by pain that interferes with daily activities rather than mere tenderness deserves medical attention. Unusual symptoms such as nipple discharge, especially if bloody or containing pus, should never be ignored as they may signal more serious conditions.
Other concerning signs include hard or irregular lumps within the breast tissue, skin changes such as dimpling or puckering, and nipple inversion that wasn’t previously present. The presence of enlarged lymph nodes in the armpit or any breast changes in men over 50 years old should prompt immediate medical evaluation to rule out malignancy. While breast cancer in men is rare, accounting for less than 1% of all breast cancer cases, vigilance remains important, particularly in those with family histories of breast cancer.
Identifying Prodromes of Gynecomastia
The early identification of gynecomastia begins with self-examination. Men should periodically check for tissue development or changes beneath the nipple and areola. A telltale sign is the presence of a disk-like mound of firm tissue directly beneath the nipple area that can be distinguished from the surrounding fatty tissue. This tissue often feels more dense and defined than normal chest fat.
Hormonal imbalance indicators frequently accompany early gynecomastia. These may include decreased libido, fatigue, hair loss, or mood changes. In adolescents, gynecomastia often coincides with other pubertal changes, affecting approximately 50-60% of teenage boys transiently. Adults should be particularly attentive to breast development that correlates with starting new medications, as numerous pharmaceuticals including certain antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications, antibiotics, heart medications, and prostate cancer treatments can trigger gynecomastia. Recent weight changes or the use of recreational drugs and alcohol can also contribute to hormonal imbalances leading to breast tissue development.
Early Symptoms of Gynecomastia and Pain Relief
Pain or tenderness is present in approximately 70% of early gynecomastia cases. This discomfort typically manifests as increased sensitivity to touch or pressure against the chest. For many men, this symptom proves more distressing than the visual changes. Most report the discomfort as a dull ache rather than sharp pain, though intensity varies considerably between individuals. Physical activities involving chest movement or contact may exacerbate symptoms.
For pain relief during early stages, several approaches may help. Non-prescription anti-inflammatory medications like ibuprofen can reduce both inflammation and discomfort. Cold compresses applied for 15-20 minutes several times daily often provide temporary relief. Avoiding stimulants like caffeine, which can increase sensitivity, may benefit some patients. Wearing a compression shirt or garment designed for gynecomastia can provide both physical support and reduced friction. For persistent pain, medical evaluation is essential, as prescription medications targeting hormonal causes might be appropriate. It’s important to note that pain typically diminishes as the condition stabilizes, even if the tissue enlargement persists.
Treatment Options for Male Breast Pain from Gynecomastia
When conservative measures prove insufficient, medical treatments for gynecomastia focus on addressing underlying causes and alleviating symptoms. For mild to moderate cases, medication options include selective estrogen receptor modulators like tamoxifen, which can reduce breast tissue and associated pain. Aromatase inhibitors may help by blocking the conversion of testosterone to estrogen. These pharmaceutical approaches are most effective when the condition has been present for less than 12 months.
Surgical intervention becomes appropriate for persistent gynecomastia causing significant physical or psychological distress. The primary surgical approaches include:
-
Liposuction: Removes fatty tissue but not glandular breast tissue
-
Mastectomy: Removes the breast gland tissue through small incisions
-
Combined approaches: Address both glandular tissue and excess fat
For severe cases with significant excess skin, more extensive procedures may include skin reduction and nipple repositioning. Recovery typically requires 1-2 weeks before returning to normal activities, with compression garments worn for several weeks post-operation. Most surgical outcomes show high satisfaction rates, with studies reporting 90-95% of patients satisfied with their results.
Breast reduction surgery costs vary considerably based on geographical location, surgeon expertise, and procedure complexity. Patients should consult with board-certified plastic surgeons who specialize in male chest procedures for optimal outcomes.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.