Understanding Osteoarthritis Treatment Options: A Comprehensive Guide
Osteoarthritis results from cartilage wear that can cause joint pain and stiffness. Management options include low-impact activity, weight support, assistive devices, medication, and, in some cases, procedures. An individualized care plan can help maintain mobility and daily comfort.
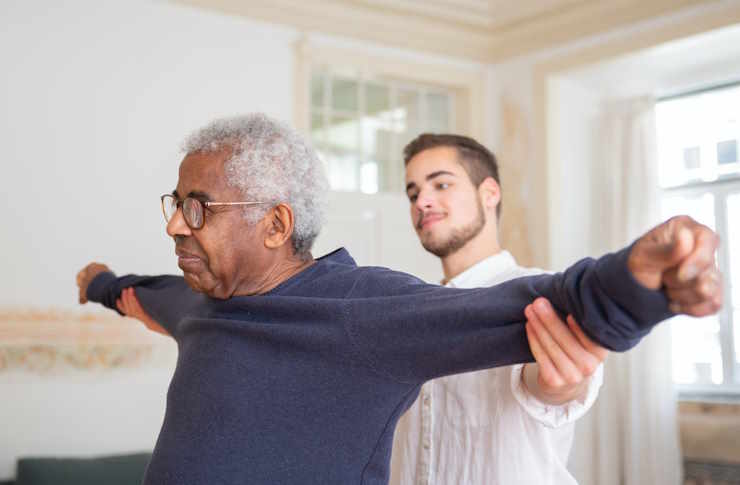

Conservative Treatment Approaches
The first line of defense against osteoarthritis typically involves non-invasive treatments. Regular physical activity, particularly low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling, helps maintain joint flexibility and strengthen supporting muscles. Weight management is crucial as excess pounds put additional stress on weight-bearing joints. Physical therapy can teach specific exercises and techniques to improve joint function and reduce pain.
Medication Options for Osteoarthritis
Several medications can help manage osteoarthritis symptoms. Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen can reduce pain and inflammation. Topical treatments, including creams and gels containing NSAIDs or capsaicin, provide localized relief. For more severe cases, doctors may prescribe stronger pain medications or corticosteroid injections directly into affected joints.
Lifestyle Modifications and Support
Daily lifestyle adjustments play a vital role in managing osteoarthritis. Using assistive devices like canes, walkers, or specially designed tools can reduce joint stress during daily activities. Proper posture and body mechanics while sitting, standing, or lifting can minimize joint strain. Heat and cold therapy, along with adequate rest periods, help manage pain and inflammation.
Advanced Treatment Options
When conservative treatments prove insufficient, advanced interventions may be considered. Viscosupplementation involves injecting hyaluronic acid into affected joints to improve lubrication. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy uses a patient’s own blood components to potentially stimulate healing. For severe cases, surgical options such as joint replacement may be recommended.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies
Many people find relief through alternative treatments. Acupuncture, massage therapy, and tai chi can help reduce pain and improve joint function. Nutritional supplements like glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate are popular, though evidence for their effectiveness varies. Always consult healthcare providers before starting any alternative treatments.
Treatment Cost Considerations
Treatment costs vary significantly based on the approach chosen and location of care:
| Treatment Type | Average Cost Range | Insurance Coverage |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Therapy | $50-150 per session | Often partially covered |
| OTC Medications | $10-30 monthly | Not typically covered |
| Corticosteroid Injection | $100-300 per injection | Usually covered |
| Joint Replacement | $20,000-50,000 | Typically covered with copay |
| Alternative Therapies | $40-120 per session | Limited coverage |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Managing osteoarthritis often requires a combination of treatments tailored to individual needs, severity of symptoms, and lifestyle factors. Success typically comes from working closely with healthcare providers to develop and adjust treatment plans over time as symptoms and needs change.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.